Garden School / Beijing No.4 High School Fangshan Campus
Situated in the center of a new town just outside Beijing’s southwest fifth ring road, this new public school on 4.5 hectares of land is designed as the branch campus for the renowned Beijing No.4 High School. As an important piece in a grand scheme to build a healthier and self-sustainable new town, avoiding problems of the earlier mono-functional suburban developments, the school is vital to the newly urbanized surrounding area.
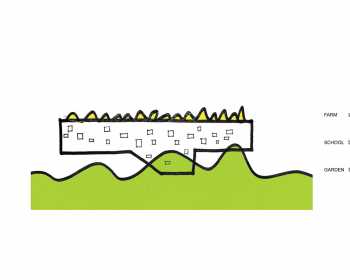
The intention of creating more open spaces filled with nature, something that urban Chinese students today desperately need, combined with the space limitations of the site, inspired a strategy on the vertical dimension to create multiple grounds, by separating the programs into above and below, and inserting gardens in-between. The juxtaposition of the resultant upper and lower building, connected at the ‘middle-ground’ in various ways, is as much an interesting spatial strategy as a signifier of the relationship between formal and informal educational spaces in the new school.
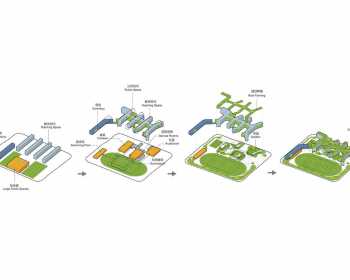
The lower building contains large and non-repetitive public functions of the school, such as the canteen, the auditorium, the gymnasium, and the swimming pool. Each of these spaces with their varying height requirements, push the ground up from below into various mound shapes that touch the belly of the upper building; their roofs in the form of landscaped gardens become the undulating new open ‘ground’. The upper building is a thin rhizome shaped slab that contains the more repetitive and rigid programs of classrooms, labs, dormitories and administration. Its mega form extends, bends, and branches, but all connected together. The main circulation spine within this mega structure is widened to allow rapid foot traffic during class breaks. It also accommodates some semi-enclosed spaces for small group activities, like a river with organic shaped islands. The roof-top of the upper building is designed to be an organic farm, with 36 plots for the 36-classes of students in the school, providing students the chance to learn the techniques of farming, and also paying tribute to the site’s pastoral past.
The contrast between the two types of educational spaces and the rich mix of programs within create a surprising spatial complexity. With the unique character for each different space, an urban experience is created within this complex of education facilities. Unlike a typical campus with hierarchical spatial organization and often clear axis to organize more or less symmetrical movements, this new school is free form and meant to have multiple centers that can be accessed in any possible sequences. It is a place with a free spirit that encourages explorations and awaits reinventions by different individuals. Hopefully the physical environment can inspire and initiate some much needed changes in the education system of China today.
This project aims to be the first triple-green-star rated school in the country (a standard that exceeds LEED Gold). In order to maximize natural ventilation and natural light, and minimize heat gain during summer and heat loss in the winter, passive solar strategies are adopted in almost all aspects of the design, from the planning of the building geometry all the way to the details of the window design. Permeable ground surface paving and expansive green roofs helps to minimize surface run-off, and three large underground water retention basins collect precious rain water from the athletics field for irrigation of the farms and gardens. A geothermal ground-source heat pump provides a sustainable source of energy for the large public spaces, whilst independently controlled VRV units serve all the individual teaching spaces to ensure flexible operation. Throughout the project, simple, natural, and durable materials such as bamboo plywood, pebble dashing (a vanishing technique), stone, and exposed concrete are used.
In the contemporary Chinese context, arguably the most pertinent issue and challenge is that of the relationship among individual, society, and nature. Education bears great responsibilities. It is to these issues that this new campus project aspires to be both a touchstone and a response.
| The Plan | TYPOLOGY, CONSTRUCTION AND SOCIAL RELEVANCE call_made
| Dwell | The Great 88, Today’s Most Inspiring People, Products and Projects call_made
| Dwell | The Great 88, Today’s Most Inspiring People, Products and Projects call_made
| Archdaily | Beijing No.4 High School Fangshan Campus / OPEN Architecture call_made
| Designboom | OPEN architecture creates garden-like fangshan high school in beijing call_made
| dezeen | OPEN Architecture completes a "free-form" Beijing School Surrounded by Gardens call_made
| Designboom | OPEN architecture + spirit of space present a visual manifesto on chinese architecture call_made
| Architectural Journal | Beijing No.4 High School Fangshan Campus call_made
| Archdaily | Beijing No.4 High School Fangshan Campus / OPEN Architecture call_made
| Designboom | OPEN architecture + spirit of space present a visual manifesto on chinese architecture call_made
| dezeen | OPEN Architecture completes a "free-form" Beijing School Surrounded by Gardens call_made
| Designboom | OPEN architecture creates garden-like fangshan high school in beijing call_made
| Architectural Record | Garden School | Branching Out call_made
| Arcasia Awards Finalist call_made
| Bronze American Architecture Prize call_made
| Architizer A+ Awards Finalist call_made
| The Creation Gold Awards from Architectural Society of China call_made
| London Design Museum's Designs of the Year 2015 Nomination (US) call_made
| The Merit Award of 2015 AIANY Design Awards (US) call_made
Facts
Year:
Location: Beijing, China
Floor area: 57,773
Site area: -
Type: Architecture
Client: Changyang Government of Fangshan District, Beijing
Status: Completed